In a country as diverse as India, where culture, traditions, and history play significant roles, the concept of caste remains deeply ingrained in society. The caste system, a social stratification that dates back thousands of years, still influences many aspects of life, including marriage, education, and employment. Last names, often indicative of one’s caste, are a key component in understanding this intricate social structure. This article delves into the significance of last names in relation to caste, offering insights into their origins, meanings, and implications.
For those looking to understand the Indian caste system through last names, the task can be daunting. The diversity of India’s population means that surnames can vary greatly depending on region, religion, and language. Furthermore, the same surname might belong to different castes in various parts of the country. As such, a systematic approach to examining last names is essential for anyone interested in comprehending how they relate to caste.
This guide on ‘Indian Last Name Caste Lookup’ provides a detailed analysis of the connection between surnames and caste identities. From exploring the historical context of the caste system to understanding the modern-day implications of last names, this article serves as an invaluable resource. Whether you are a researcher, a student, or someone with a keen interest in Indian culture, this comprehensive guide aims to enhance your knowledge and understanding of the intricate tapestry that is India’s caste system.
Read also:Insightful Journey Into The Life And Achievements Of Iga Obrycka
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Caste System in India
- Historical Evolution of the Indian Caste System
- Role of Last Names in Caste Identification
- Regional Variations in Last Names
- Impact of Religion on Last Names and Caste
- Common Indian Last Names and Their Caste Links
- How to Conduct an Indian Last Name Caste Lookup?
- Challenges in Determining Caste from Last Names
- Modern Perspectives on Caste and Last Names
- Caste System and Its Social Implications
- Government Policies and Caste Classification
- Tools and Resources for Caste Research
- Can Last Names Determine Social Status?
- Future of the Caste System in India
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Understanding the Caste System in India
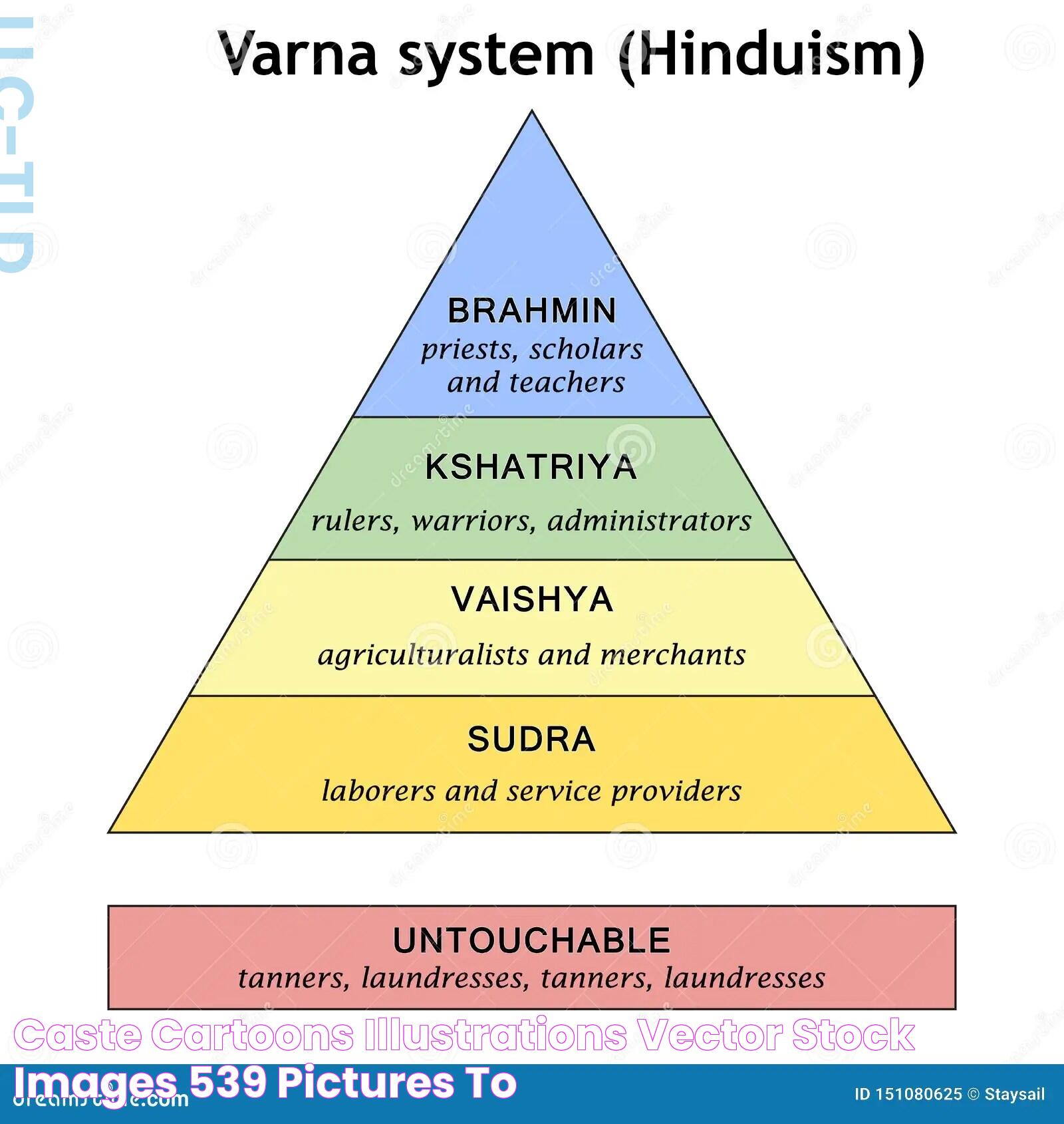
The caste system in India is one of the world’s oldest forms of social stratification, deeply embedded in the country's history and culture. It divides people into hierarchical groups based on their karma (work) and dharma (duty), as described in ancient Indian scriptures. Traditionally, the system is divided into four main categories: Brahmins (priests and teachers), Kshatriyas (warriors and rulers), Vaishyas (traders), and Shudras (laborers). Additionally, there are Dalits, formerly known as 'untouchables', who fall outside these categories.
Understanding the caste system is crucial for comprehending the social dynamics in India. Each caste comes with its own social status, duties, and restrictions, which have been passed down through generations. This rigid structure has historically dictated various aspects of life, including occupation, marriage, and dietary habits.
Despite legal measures and social reforms aimed at eradicating caste-based discrimination, the system still influences many facets of Indian society today. Caste-related information is often reflected in last names, making them an important indicator of one’s social identity.
Historical Evolution of the Indian Caste System
The origins of the caste system in India can be traced back to ancient times, with references found in texts such as the Rigveda, one of the oldest known Indian scriptures. Over time, what began as a flexible social structure based on occupation and duty gradually became more rigid and hereditary.
During the Vedic period, caste distinctions were based more on profession than birth. However, the arrival of the Manusmriti, an ancient legal text, institutionalized the caste system by prescribing strict rules for each caste and forbidding inter-caste marriages and interactions.
With the advent of British colonial rule, the caste system underwent further changes. The British administration’s classification of the population into rigid categories for census purposes reinforced caste identities. This period also witnessed the introduction of caste-based reservations in education and employment, aimed at uplifting marginalized communities.
Read also:Celebrate National Hot Chocolate Day With A Warm Cup Of Joy
Today, while the caste system is not as rigid as it once was, it continues to play a significant role in social and political life in India.
Role of Last Names in Caste Identification
In India, last names are often indicative of an individual's caste and can provide a wealth of information about their ancestry and social status. Surnames are typically derived from a variety of sources, including occupation, geographic origin, or the name of an ancestor.
For instance, names like Sharma, Pandey, and Mishra are commonly associated with the Brahmin caste, while names such as Singh and Chauhan are linked with Kshatriyas. Similarly, surnames like Gupta and Agarwal are often associated with the Vaishya caste.
However, it is important to note that the same surname can belong to different castes in different regions. For example, the surname 'Patel' is associated with the Patidar caste in Gujarat but is also used by other communities in different states.
Understanding the role of last names in caste identification requires knowledge of regional and historical contexts, as well as an awareness of the fluidity and complexity of caste identities.
Regional Variations in Last Names
India’s vast geographical and cultural diversity has resulted in a wide array of regional variations in last names. Each region has its own unique set of surnames that reflect its linguistic, cultural, and social nuances.
In the South, names like Iyer and Nair are prevalent among Brahmins and Kshatriyas, respectively. In the North, names like Choudhary and Yadav are common among the agrarian communities. Eastern India, including states like West Bengal, has last names such as Banerjee and Mukherjee, often associated with the Brahmin community.
Western India, particularly Maharashtra, boasts surnames like Deshmukh and Patil, which indicate land ownership and administrative roles. Meanwhile, in Rajasthan, names like Rathore and Sisodia signify royal lineage and warrior status.
These regional variations highlight the complexity and diversity of Indian surnames, making it essential to consider geographical context when conducting a caste lookup based on last names.
Impact of Religion on Last Names and Caste
Religion plays a significant role in shaping the last names and caste identities in India. Hinduism, being the predominant religion, has the most notable influence on the caste system and associated surnames. However, other religions such as Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, and Buddhism also exhibit unique naming conventions tied to community and caste.
Muslim last names like Khan, Syed, and Sheikh often indicate lineage and tribal affiliation rather than caste, reflecting Islamic teachings that discourage caste distinctions. Christian names in India, such as D’Souza and Fernandes, may have colonial influences or denote regional identity rather than caste.
Sikh surnames, like Singh and Kaur, are used universally across the community to promote equality and eliminate caste distinctions, in line with Sikh teachings. Buddhism, which originated as a reformist movement against Hindu caste practices, generally does not emphasize caste-based surnames.
Despite these differences, inter-religious interactions and conversions have resulted in overlapping and shared surnames across religions, further complicating caste identification through last names.
Common Indian Last Names and Their Caste Links
Understanding the link between common Indian last names and caste can provide valuable insights into social structures and heritage. Here are some prevalent surnames and their typical caste associations:
- Sharma: Typically Brahmin, especially in North India.
- Singh: Often associated with Kshatriyas, widely used among Rajputs and Sikhs.
- Patel: Primarily used by the Patidar community in Gujarat, but also found in other regions.
- Choudhary: Common among agrarian communities, particularly in North India.
- Nair: Associated with the warrior class in Kerala.
- Gupta: Typically linked with the Vaishya or trading community.
- Mukherjee: Predominantly Brahmin, especially in West Bengal.
It is important to recognize that these associations are not absolute and can vary based on regional and historical factors. The same surname may have different caste affiliations in different parts of India.
How to Conduct an Indian Last Name Caste Lookup?
Conducting a caste lookup based on last names can be a complex task, given the diversity and nuances of Indian surnames. Here are some steps to guide you in this process:
- Research the Name’s Origin: Begin by understanding the linguistic and geographic origins of the surname. This can provide initial clues about its caste associations.
- Consult Historical Records: Historical texts, census data, and genealogical records can offer insights into the traditional caste affiliations of certain surnames.
- Use Online Databases: Several online platforms provide databases and forums where you can query surnames and their caste links. Ensure the sources are credible and well-researched.
- Seek Expert Opinions: Engaging with historians, anthropologists, or community elders can offer valuable perspectives on the caste associations of a surname.
- Consider Regional Variations: Remember that the same surname may have different caste links in various regions. Contextualize your findings accordingly.
While these steps can aid in a caste lookup, it is crucial to approach the task with sensitivity and respect for cultural and social diversity.
Challenges in Determining Caste from Last Names
Identifying caste based on last names poses several challenges due to the complexity and fluidity of India’s social structure. Some of these challenges include:
- Regional Differences: As mentioned earlier, the same surname may belong to different castes in different regions, making it difficult to ascertain caste accurately.
- Changes Over Time: Over centuries, families have migrated, intermarried, and changed professions, leading to shifts in caste associations for certain surnames.
- Common Surnames Across Castes: Some surnames, like ‘Singh’ and ‘Patel,’ are common across multiple castes and communities, complicating caste identification.
- Social Reforms and Changes: Social reforms aimed at reducing caste discrimination have encouraged individuals to adopt different surnames or drop caste-indicative names altogether.
These challenges highlight the need for a nuanced and informed approach when attempting to determine caste based on last names.
Modern Perspectives on Caste and Last Names
In contemporary India, perspectives on caste and last names are evolving, influenced by social reforms, education, and globalization. While the traditional caste system still holds sway in many areas, there is a growing movement towards de-emphasizing caste identities.
Urbanization and increased exposure to global cultures have led to a more fluid understanding of identity, with many people choosing to identify themselves based on profession, education, or personal achievements rather than caste.
Numerous social and political movements advocate for the abolition of caste-based discrimination, promoting equality and social justice. Consequently, there is a rise in the number of individuals who either modify their last names to obscure caste identity or adopt surnames that reflect personal or familial values.
This shift in attitudes is gradually reshaping the traditional narrative surrounding caste and last names in India, paving the way for a more inclusive society.
Caste System and Its Social Implications
The caste system, despite being officially abolished, continues to exert a significant influence on social and economic dynamics in India. It impacts various aspects of life, including:
- Marriage: Caste remains a key factor in matrimonial alliances, with many families preferring intra-caste marriages to preserve cultural and social ties.
- Education: Caste-based reservations in educational institutions aim to provide opportunities to historically marginalized communities, but they also spark debates on meritocracy and equality.
- Employment: Although illegal, caste discrimination persists in some workplaces, affecting job opportunities and career advancement for individuals from lower castes.
- Politics: Caste affiliations often influence voting patterns and political alignments, with caste-based parties playing a significant role in regional and national politics.
The social implications of the caste system underscore the importance of continued efforts towards achieving equality and eliminating caste-based discrimination.
Government Policies and Caste Classification
The Indian government has implemented various policies and legal measures to address caste-related issues and promote social justice. These include:
- Reservation System: The government reserves a percentage of seats in educational institutions and government jobs for Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), and Other Backward Classes (OBC) to uplift historically oppressed communities.
- Legal Framework: Laws such as the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act aim to protect marginalized communities from discrimination and violence.
- Census and Classification: The government conducts a caste-based census to gather data on the socio-economic status of different communities, aiding in policy formulation.
While these policies have made significant strides in promoting equality, challenges remain, necessitating ongoing efforts to ensure their effective implementation and address emerging issues.
Tools and Resources for Caste Research
For researchers and individuals interested in exploring caste and last names, several tools and resources can aid in their study:
- Online Databases: Websites and platforms like the National Archives of India and genealogy databases provide access to historical records and family trees.
- Academic Journals: Scholarly articles and papers offer in-depth analyses and insights into caste dynamics and surname associations.
- Books and Publications: Books such as "The Annihilation of Caste" by B.R. Ambedkar provide historical context and critique of the caste system.
- Community Forums: Online forums and discussion groups facilitate knowledge-sharing and collaboration among individuals researching caste and surnames.
These resources can enhance understanding and provide valuable information for those studying the complex interplay between caste and last names in India.
Can Last Names Determine Social Status?
While last names can offer insights into an individual’s caste and heritage, they are not definitive indicators of social status. Several factors contribute to determining social status, including:
- Education: Educational attainment is a significant determinant of social status, with higher education often leading to better employment opportunities and social mobility.
- Profession: An individual’s profession and economic standing play a crucial role in shaping their social status.
- Personal Achievements: Recognition and achievements in various fields, such as arts, sports, or business, can elevate an individual’s social standing.
- Social Networks: Connections and relationships within influential social or professional circles can impact one’s social status.
Therefore, while last names can provide context, they are not the sole determinants of an individual’s social status, highlighting the dynamic and multifaceted nature of identity in modern society.
Future of the Caste System in India
The future of the caste system in India is subject to ongoing debate and speculation. While traditional caste identities continue to hold significance for many, there is a noticeable shift towards a more egalitarian society.
Several factors contribute to this changing landscape:
- Education and Awareness: Increasing education and awareness are challenging traditional caste norms, promoting equality and inclusivity.
- Economic Development: Economic growth and globalization are leading to greater social mobility, reducing the emphasis on caste-based identities.
- Youth Perspectives: Younger generations are more likely to question and reject caste-based discrimination, advocating for social change and justice.
- Policy Reforms: Government policies aimed at promoting equality and social justice continue to shape the future of caste dynamics in India.
Despite these positive trends, challenges remain, necessitating sustained efforts to address caste-related issues and foster a more inclusive and equitable society.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the significance of last names in the Indian caste system?
Last names in India often indicate an individual's caste, providing insights into their ancestry and social status. They can reflect occupation, geographic origin, or lineage.
2. Can two people with the same last name belong to different castes?
Yes, the same surname can belong to different castes in various regions. Regional and historical contexts play a crucial role in determining caste affiliations.
3. How do social reforms impact caste and last names in India?
Social reforms have encouraged individuals to adopt last names that obscure caste identity, promoting equality and reducing caste-based discrimination.
4. Are there tools available for conducting a caste lookup based on last names?
Yes, tools such as online databases, academic journals, and genealogy websites can aid in researching the caste associations of last names.
5. What role does religion play in shaping last names and caste identities?
Religion significantly influences naming conventions in India. Hinduism has the most notable impact on the caste system, while other religions exhibit unique naming practices.
6. How does the reservation system affect caste dynamics in India?
The reservation system aims to uplift marginalized communities by providing opportunities in education and employment, impacting caste dynamics and social mobility.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between last names and caste in India is a testament to the country’s rich cultural heritage and diversity. While last names can provide valuable insights into caste identities, they are not definitive indicators of social status. Understanding this complex interplay requires a nuanced approach that considers historical, regional, and social factors.
As India continues to evolve and modernize, perspectives on caste and last names are gradually shifting. Education, economic development, and social reforms are promoting greater equality and inclusivity, challenging traditional norms and paving the way for a more egalitarian society.
In the journey towards a more equitable future, it is essential to recognize the progress made while acknowledging the challenges that remain. By fostering dialogue, understanding, and respect for diversity, India can aspire to a society where caste-based discrimination is a relic of the past, and equality prevails.