The Second World War, a conflict that engulfed the globe from 1939 to 1945, remains one of the most devastating events in human history. The sheer scale of destruction, loss of life, and impact on nations was unprecedented. Among the many countries affected, Germany, both as a perpetrator and a victim, experienced profound consequences. The german death toll ww2 is a topic that reflects the war's far-reaching effects on the German population, highlighting not just the military losses, but also the civilian casualties, and the long-term ramifications. Understanding these figures provides insight into the immense human cost of the war, and the tragedy that befell millions of families.
Germany's involvement in World War II was marked by aggressive expansionism and the pursuit of an ideologically driven war. This led to catastrophic losses, not only on the battlefield but also within its own borders. The german death toll ww2 encompasses a broad spectrum of losses, including soldiers, civilians, and victims of the Nazi regime. Analyzing these figures reveals the multifaceted impacts of the war on Germany's demographic landscape. The aftermath of the war saw millions of Germans displaced, cities in ruins, and a society grappling with the consequences of its actions and the immense loss of life.
In the post-war period, Germany faced the daunting task of rebuilding a nation from the ashes of destruction. The german death toll ww2 serves as a somber reminder of the war's human cost and the need for reflection and remembrance. It also underscores the importance of peace and reconciliation in the years that followed. The legacy of these losses continues to influence German society and its approach to international relations, emphasizing a commitment to peace and unity in a once-divided nation.
Read also:Alabama Basketball Triumphs Traditions And Tactics
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| 1. Understanding the German Death Toll WW2 |
| 2. What Events Led to the High German Death Toll? |
| 3. Military Losses: The German Armed Forces |
| 4. Civilian Casualties: The Home Front |
| 5. The Holocaust and Its Impact on German Society |
| 6. How Did the War Affect German Demographics? |
| 7. Post-War Consequences: Rebuilding Germany |
| 8. German POWs and Their Treatment |
| 9. The Role of Allied Bombing Campaigns |
| 10. How Did German Society Cope with Loss? |
| 11. The Psychological Impact on Survivors |
| 12. German Death Toll WW2: A Historical Perspective |
| 13. Lessons Learned: Preventing Future Conflicts |
| 14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
| 15. Conclusion: The Legacy of the German Death Toll WW2 |
Understanding the German Death Toll WW2
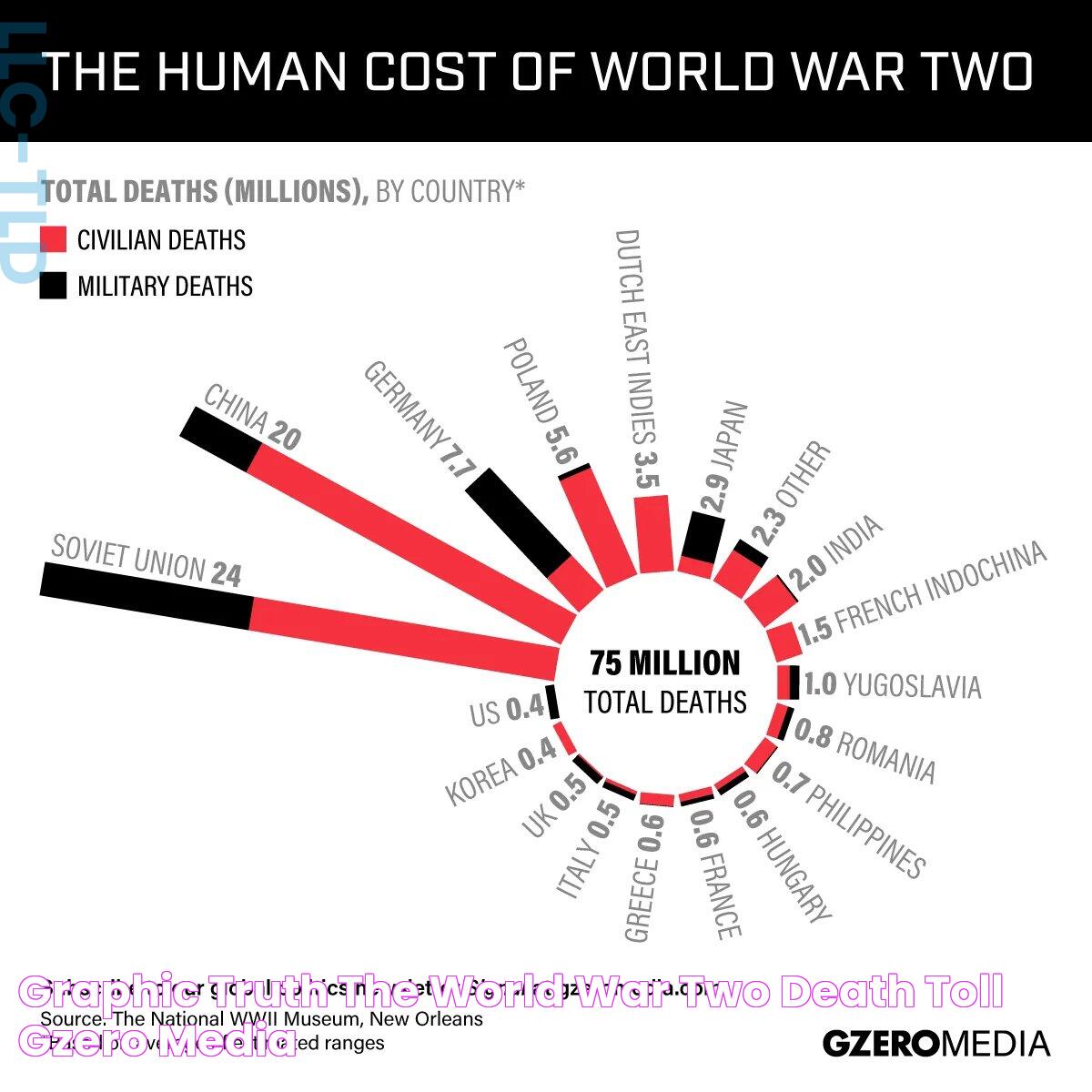
The german death toll ww2 is a complex and multifaceted subject that encompasses both military and civilian casualties. It is estimated that approximately 5.3 million German soldiers and around 1.5 million civilians lost their lives during the conflict. These figures are not merely numbers; they represent the profound loss and suffering experienced by countless families across Germany. The impact of these losses was felt acutely in the years following the war, as the nation grappled with the consequences of its actions and the devastation left in its wake.
Several factors contributed to the high german death toll ww2. The aggressive military campaigns led by Nazi Germany resulted in significant military casualties. The conscription of millions of young men into the armed forces meant that families across the country were directly affected by the loss of loved ones. Furthermore, the war also brought about widespread destruction within Germany itself, as cities were bombed, and civilians were caught in the crossfire.
The Holocaust, one of the darkest chapters in human history, also had a significant impact on the german death toll ww2. While the majority of the victims were from various ethnic and religious minorities, a substantial number of ethnic Germans who opposed the Nazi regime or did not fit the Aryan ideal also perished in concentration camps. This adds another layer of complexity to understanding the full extent of the german death toll ww2.
What Events Led to the High German Death Toll?
Several pivotal events contributed to the high german death toll ww2. The initial invasion of Poland in 1939 marked the beginning of a series of aggressive military campaigns that saw German forces engaged on multiple fronts. The subsequent invasions of France, the Soviet Union, and other European countries stretched German military resources thin and resulted in significant casualties.
The turning point of the war came with the Battle of Stalingrad in 1942-1943, where the German Army suffered a catastrophic defeat at the hands of the Soviet Union. This battle alone accounted for hundreds of thousands of German military casualties, as the harsh winter and relentless Soviet resistance took a heavy toll on German forces.
The Allied bombing campaigns on German cities also played a significant role in increasing the german death toll ww2. Cities such as Dresden, Hamburg, and Berlin were heavily bombed, resulting in massive civilian casualties and widespread destruction. The firebombing of Dresden in February 1945, in particular, stands out as one of the most devastating attacks, with estimates of civilian deaths ranging from 25,000 to 35,000.
Read also:Delving Into The Exciting World Of Pumas Toluca Clash
Military Losses: The German Armed Forces
The german death toll ww2 is often associated with the heavy military losses suffered by the German Armed Forces. The Wehrmacht, Germany's unified armed forces, faced immense challenges as they engaged in battles across Europe and beyond. The German military strategy, which initially relied on rapid, decisive victories, eventually led to prolonged conflicts that depleted resources and manpower.
German soldiers fought in various theaters of war, including North Africa, the Eastern Front, and Western Europe. The harsh conditions on the Eastern Front, in particular, resulted in significant casualties. The Battle of Stalingrad, as mentioned earlier, was a turning point where German forces suffered one of their most significant defeats, with over 300,000 soldiers killed, wounded, or captured.
As the war progressed, the German military faced shortages of supplies, equipment, and manpower. This led to the conscription of younger and older men, as well as the use of forced labor from occupied territories. Despite these efforts, the german death toll ww2 continued to rise as the war dragged on, with the eventual collapse of the Nazi regime in May 1945.
Civilian Casualties: The Home Front
While the german death toll ww2 is often associated with military losses, civilian casualties also played a significant role. The war brought unprecedented destruction to German cities and towns, with millions of civilians affected by the conflict.
Allied bombing campaigns targeted key industrial and military sites, but often resulted in widespread destruction of civilian areas. The firebombing of cities like Dresden and Hamburg led to tens of thousands of civilian deaths, as residential areas were reduced to rubble.
The disruption of daily life during the war also contributed to civilian casualties. Shortages of food, medicine, and other essential supplies led to malnutrition and disease, particularly in the later stages of the war. The German population faced immense hardships, as the war took a toll on the home front.
The Holocaust and Its Impact on German Society
The Holocaust was one of the most horrific events of World War II, re