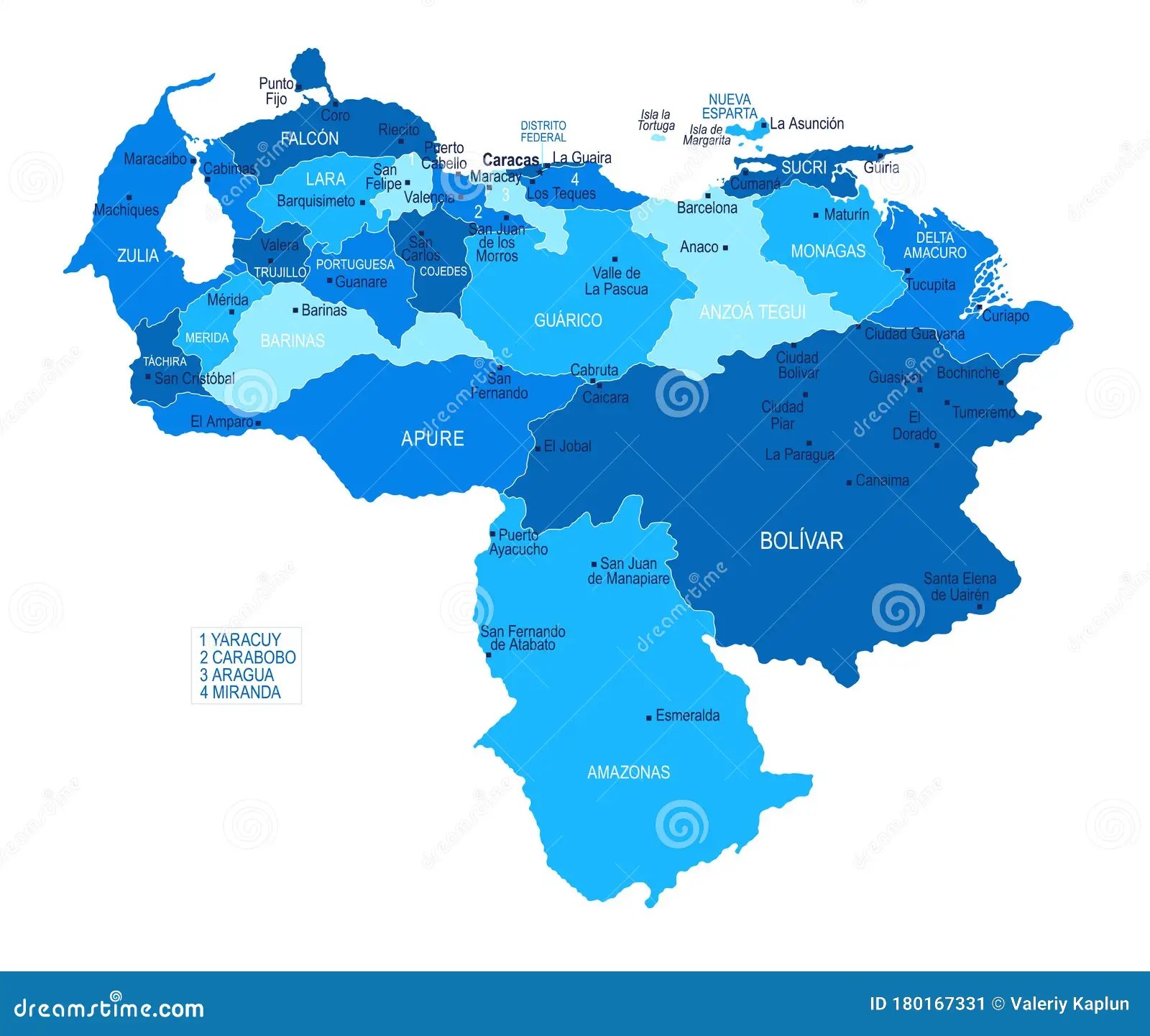
Venezuela, a country located on the northern coast of South America, is known for its stunning natural beauty and diverse cultural heritage. The regions of Venezuela present a tapestry of landscapes ranging from the Andean mountains to lush Amazonian rainforests, and from the Caribbean coastlines to the vast plains of the Llanos. Each region offers its unique blend of ecological wonders, cultural diversity, and historical significance, making Venezuela a truly remarkable place to explore. With its vast and varied geography, the regions of Venezuela provide an abundance of opportunities for adventure, exploration, and cultural discovery.
Understanding the regions of Venezuela is essential for anyone looking to delve into the country’s rich natural and cultural offerings. This article will take you on a journey through the major regions, highlighting what makes each area distinct and noteworthy. From the bustling urban centers to the serene rural landscapes, Venezuela's regions encapsulate the essence of this vibrant nation. Whether you are a nature enthusiast, a history buff, or simply someone seeking to learn more about this fascinating country, the regions of Venezuela have something to offer everyone.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various regions of Venezuela, delving into their geographical features, cultural attributes, and economic significance. We will also address common questions about these regions and provide insights backed by first-hand knowledge and credible sources. Join us as we uncover the captivating regions of Venezuela, each with its own story to tell and treasures to reveal.
Read also:Analyzing The Dynamics Of Aa Stock Market Insights And Future Outlook
Table of Contents
- Andes Region: Where Mountains Meet Culture
- The Llanos Region: Venezuela’s Vast Plains
- Amazon Region: A Lush Green Paradise
- Caribbean Coast: Sun, Sand, and Sea
- Orinoco Delta: A Waterway Wonderland
- Central Region: The Heart of Venezuela
- Guayana Region: Rich in Resources and History
- Maracaibo Basin: Oil and Culture
- Los Roques Archipelago: A Caribbean Gem
- How do the regions of Venezuela influence culture?
- What is the economic impact of Venezuela's regions?
- What makes Venezuela's biodiversity unique?
- What challenges do the regions of Venezuela face?
- Tourism in Venezuela: Discovering its Regions
- FAQs about the Regions of Venezuela
- Conclusion: Embracing Venezuela's Regional Diversity
Andes Region: Where Mountains Meet Culture
The Andes Region of Venezuela is a breathtaking area characterized by towering mountain ranges, lush valleys, and a unique cultural heritage. Spanning the states of Mérida, Táchira, and Trujillo, this region is home to some of the highest peaks in the country, including the famous Pico Bolívar. The Andes offer a climate that ranges from cool and temperate in the mountains to warmer and more humid in the lower valleys, providing a diverse array of ecosystems and agricultural opportunities.
In the Andes, you'll find picturesque towns and cities that reflect the region's rich history and cultural traditions. Mérida, known as the "City of Gentlemen," is the cultural and educational hub of the region, with its prestigious University of the Andes and vibrant arts scene. The city is also a gateway to the Andes' stunning natural attractions, such as the Sierra Nevada National Park and the Mérida Cable Car, the longest and highest cable car in the world.
The Andes Region is also renowned for its agricultural productivity, particularly the cultivation of coffee, fruits, and vegetables. Traditional Andean cuisine features hearty dishes made with locally sourced ingredients, such as arepas, hallacas, and pabellón criollo. The region's cultural festivals, including the Feria Internacional de San Sebastián and the Paradura del Niño, showcase the vibrant traditions and customs of the Andean people.
Whether you're an outdoor enthusiast seeking adventure in the mountains or a cultural traveler interested in exploring the region's rich heritage, the Andes Region of Venezuela offers a captivating blend of natural beauty and cultural richness that is sure to leave a lasting impression.
The Llanos Region: Venezuela’s Vast Plains
The Llanos Region of Venezuela is an expansive area of flat, grassy plains that stretch across the central part of the country. Known for its vast open landscapes and rich biodiversity, the Llanos are a vital part of Venezuela's natural and cultural identity. This region is primarily located in the states of Apure, Barinas, Cojedes, Guárico, and Portuguesa, and is characterized by its seasonal flooding and unique ecosystems.
The Llanos Region is often referred to as the "breadbasket" of Venezuela due to its agricultural importance. The fertile soils and favorable climate make it an ideal location for cattle ranching, rice cultivation, and the production of other crops such as corn and sugarcane. The traditional cowboy culture, known as "llanero," is an integral part of the region's identity, with its own distinct music, dance, and folklore.
Read also:Lewis Pullman A Rising Star In Hollywoods Firmament
Wildlife enthusiasts will be delighted by the Llanos' incredible biodiversity, which includes species such as capybaras, jaguars, anacondas, and a wide variety of bird species. The region's wetlands and rivers are home to unique ecosystems that support a diverse array of flora and fauna. National parks such as the Hato El Frío and the Aguaro-Guariquito National Park offer opportunities for wildlife viewing and eco-tourism.
The Llanos Region's open skies and stunning sunsets provide a perfect backdrop for outdoor adventures and exploration. Whether you're interested in birdwatching, horseback riding, or simply enjoying the tranquility of the plains, the Llanos offer a unique and unforgettable experience.
Amazon Region: A Lush Green Paradise
The Amazon Region of Venezuela is a lush and remote area characterized by its dense rainforests, winding rivers, and rich biodiversity. Covering the state of Amazonas, this region is part of the larger Amazon Basin, which extends across several South American countries. The Amazon Region is known for its vibrant ecosystems, indigenous cultures, and stunning natural beauty.
As one of the most biologically diverse regions on the planet, the Amazon is home to an incredible array of plant and animal species. The region's rainforests are teeming with life, including jaguars, pink river dolphins, macaws, and countless species of insects and amphibians. The rivers and tributaries that flow through the Amazon provide essential habitats for aquatic life and serve as vital transportation routes for the region's inhabitants.
The indigenous communities of the Amazon Region have lived in harmony with the land for centuries, preserving their traditional ways of life and cultural practices. These communities offer valuable insights into sustainable living and the importance of biodiversity conservation. Visitors to the Amazon can learn about indigenous cultures, explore the region's natural wonders, and participate in eco-friendly tourism activities.
The Amazon Region's remote and pristine landscapes provide a unique opportunity for adventure and exploration. Whether you're interested in trekking through the rainforest, canoeing along the rivers, or discovering the region's cultural heritage, the Amazon offers an unparalleled experience of natural beauty and cultural richness.
Caribbean Coast: Sun, Sand, and Sea
The Caribbean Coast of Venezuela is a stunning region known for its beautiful beaches, crystal-clear waters, and vibrant coastal culture. Stretching along the northern coast of the country, this region includes the states of Zulia, Falcón, Vargas, and Anzoátegui, as well as the islands of Margarita and Los Roques. The Caribbean Coast is a popular destination for tourists seeking sun, sea, and relaxation.
Venezuela's Caribbean Coast offers a diverse array of beaches, from the bustling and lively shores of Margarita Island to the tranquil and secluded coves of Morrocoy National Park. The region is also home to vibrant coastal towns and cities, each with its own unique charm and cultural offerings. The city of Maracaibo, for example, is known for its lively music scene and rich culinary traditions, while the town of Choroní is famous for its Afro-Venezuelan heritage and colorful festivals.
The Caribbean Coast's warm and sunny climate makes it an ideal location for outdoor activities and water sports. Visitors can enjoy snorkeling, scuba diving, windsurfing, and sailing, or simply relax on the sandy beaches and soak in the sun. The region's coral reefs and marine life provide excellent opportunities for underwater exploration and eco-tourism.
Whether you're seeking adventure or relaxation, the Caribbean Coast of Venezuela offers a perfect blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and recreational opportunities. From the vibrant coastal cities to the serene island retreats, this region is a paradise for beach lovers and cultural travelers alike.
Orinoco Delta: A Waterway Wonderland
The Orinoco Delta is a vast and intricate network of waterways, channels, and islands located in eastern Venezuela. This region is defined by the mighty Orinoco River, which flows into the Atlantic Ocean, creating a dynamic and diverse ecosystem. The Orinoco Delta is a unique and captivating region, offering a fascinating blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and ecological significance.
As one of the largest river deltas in the world, the Orinoco Delta is home to a rich array of wildlife and plant species. The region's wetlands, mangroves, and forests provide essential habitats for species such as caimans, river dolphins, howler monkeys, and a wide variety of bird species. The delta's diverse ecosystems play a crucial role in supporting the region's biodiversity and maintaining the health of the surrounding environment.
The indigenous Warao people have inhabited the Orinoco Delta for centuries, living in harmony with the land and waterways. Their traditional way of life is closely tied to the natural environment, and they offer valuable insights into sustainable living and cultural preservation. Visitors to the Orinoco Delta can learn about the Warao culture, explore the region's natural wonders, and participate in eco-friendly tourism activities.
The Orinoco Delta's remote and pristine landscapes provide a unique opportunity for adventure and exploration. Whether you're interested in navigating the delta's waterways, observing the region's wildlife, or discovering its cultural heritage, the Orinoco Delta offers an unparalleled experience of natural beauty and cultural richness.
Central Region: The Heart of Venezuela
The Central Region of Venezuela is a vital and dynamic area that serves as the economic and cultural heart of the country. This region includes the capital city of Caracas, as well as the states of Aragua, Carabobo, and Miranda. The Central Region is characterized by its bustling urban centers, rich cultural heritage, and diverse landscapes.
Caracas, the capital of Venezuela, is a vibrant metropolis that serves as the political, economic, and cultural hub of the country. The city is home to a wide array of cultural attractions, including museums, theaters, and historic sites. The bustling streets of Caracas are alive with the energy of its people, offering a mix of traditional and contemporary Venezuelan culture.
The Central Region's diverse landscapes include coastal areas, mountainous regions, and fertile valleys. The region's agricultural production includes crops such as coffee, cocoa, and sugarcane, as well as a variety of fruits and vegetables. The Central Region's natural beauty is showcased in national parks such as Henri Pittier National Park and El Avila National Park, which offer opportunities for outdoor recreation and eco-tourism.
The Central Region's rich cultural heritage is reflected in its vibrant festivals, music, and culinary traditions. From the lively sounds of salsa and merengue to the delicious flavors of traditional Venezuelan cuisine, the Central Region offers a rich tapestry of cultural experiences. Whether you're exploring the urban landscapes of Caracas or the serene beauty of the surrounding countryside, the Central Region of Venezuela provides a captivating blend of culture and nature.
Guayana Region: Rich in Resources and History
The Guayana Region of Venezuela is a vast and resource-rich area located in the southeastern part of the country. This region includes the states of Bolívar, Amazonas, and Delta Amacuro, and is characterized by its diverse landscapes, abundant natural resources, and historical significance. The Guayana Region is home to some of Venezuela's most iconic natural landmarks, including Angel Falls, the world's highest waterfall, and the Gran Sabana, a stunning plateau with unique rock formations and diverse ecosystems.
The Guayana Region is a major center for mining and industrial activities, with significant reserves of minerals such as gold, bauxite, and iron ore. The region's abundant water resources are harnessed for hydroelectric power generation, contributing to Venezuela's energy supply. The Guayana Region's economic importance is matched by its rich cultural heritage, with a diverse population that includes indigenous communities and descendants of African and European settlers.
The Guayana Region's natural beauty and cultural diversity make it a popular destination for eco-tourism and adventure travel. Visitors can explore the region's national parks, such as Canaima National Park and La Gran Sabana National Park, which offer opportunities for hiking, wildlife viewing, and cultural experiences. The region's waterways, including the Orinoco and Caroní rivers, provide opportunities for water-based activities such as kayaking and fishing.
Whether you're interested in exploring the region's natural wonders, learning about its cultural heritage, or discovering its economic significance, the Guayana Region of Venezuela offers a fascinating blend of history, culture, and natural beauty.
Maracaibo Basin: Oil and Culture
The Maracaibo Basin is a region located in the northwestern part of Venezuela, centered around Lake Maracaibo, one of the largest lakes in South America. This region is known for its rich oil reserves, vibrant cultural heritage, and unique geographical features. The Maracaibo Basin includes the state of Zulia, which is a major center for oil production and economic activity in Venezuela.
Lake Maracaibo is a key feature of the region, serving as a vital transportation route and a source of livelihood for the surrounding communities. The lake is connected to the Gulf of Venezuela by the Tablazo Strait, providing access to the Caribbean Sea. The region's oil industry has played a significant role in shaping the economy and development of Venezuela, with the Maracaibo Basin being one of the country's most important oil-producing areas.
The Maracaibo Basin's cultural heritage is rich and diverse, with a mix of indigenous, African, and European influences. The city of Maracaibo, the capital of Zulia state, is known for its lively music scene, delicious cuisine, and vibrant festivals. The region's traditional music, known as "gaita," is an integral part of its cultural identity, with its lively rhythms and festive spirit.
The Maracaibo Basin's unique geographical features, including its wetlands, mangroves, and coastal areas, provide important habitats for a variety of plant and animal species. The region's natural beauty and cultural richness make it a popular destination for tourism and exploration.
Los Roques Archipelago: A Caribbean Gem
The Los Roques Archipelago is a stunning group of islands and cays located off the northern coast of Venezuela in the Caribbean Sea. This region is known for its pristine beaches, crystal-clear waters, and rich marine biodiversity. Los Roques is a popular destination for tourists seeking a tropical paradise and offers a wide range of recreational activities and eco-tourism opportunities.
The archipelago is part of the Los Roques National Park, a protected area that encompasses over 300 islands and islets. The park is home to a diverse array of marine life, including coral reefs, sea turtles, and a variety of fish species. The clear waters and abundant marine life make Los Roques a prime location for snorkeling, scuba diving, and other water-based activities.
The islands of Los Roques offer a tranquil and idyllic setting for relaxation and exploration. Visitors can enjoy the white sandy beaches, explore the coral reefs, and discover the unique flora and fauna of the region. The local community on the island of Gran Roque provides a glimpse into the traditional way of life in this remote and beautiful part of Venezuela.
Whether you're seeking adventure or relaxation, the Los Roques Archipelago offers a perfect blend of natural beauty and cultural experiences. From the vibrant marine life to the serene island landscapes, this Caribbean gem is a must-visit destination for travelers looking to experience the regions of Venezuela.
How do the regions of Venezuela influence culture?
The regions of Venezuela play a significant role in shaping the country's cultural identity and diversity. Each region has its own unique blend of cultural influences, traditions, and customs, which contribute to the rich tapestry of Venezuelan culture. From the vibrant music and dance of the Caribbean Coast to the traditional cowboy culture of the Llanos, the regions of Venezuela offer a diverse array of cultural experiences.
The Andes Region, with its rich history and cultural heritage, is known for its traditional festivals and culinary traditions. The Amazon Region, home to indigenous communities, offers valuable insights into sustainable living and cultural preservation. The Guayana Region's diverse population reflects a mix of indigenous, African, and European influences, contributing to its rich cultural heritage.
The regions of Venezuela also influence the country's music, art, and literature. Traditional music styles such as joropo, gaita, and merengue are deeply rooted in the cultural traditions of different regions, while contemporary artists draw inspiration from the diverse landscapes and cultural heritage of Venezuela.
In conclusion, the regions of Venezuela play a vital role in shaping the country's cultural identity and diversity. Each region offers its own unique blend of cultural influences, traditions, and customs, contributing to the rich tapestry of Venezuelan culture.
What is the economic impact of Venezuela's regions?
The regions of Venezuela contribute significantly to the country's economy, each playing a unique role in shaping its economic landscape. From agriculture and mining to tourism and oil production, the regions of Venezuela offer a diverse array of economic activities and opportunities.
The Llanos Region, known as the "breadbasket" of Venezuela, is a major center for agriculture and cattle ranching. The fertile plains of the Llanos support the cultivation of rice, corn, sugarcane, and other crops, making it an essential part of the country's food production and supply chain.
The Guayana Region is rich in natural resources, with significant reserves of minerals such as gold, bauxite, and iron ore. The region's mining and industrial activities contribute to Venezuela's economic growth and development, providing employment and generating revenue for the country.
The Maracaibo Basin is a major center for oil production, with rich reserves of oil and natural gas. The region's oil industry plays a vital role in shaping Venezuela's economy, contributing to its energy supply and export revenue.
The Caribbean Coast and Los Roques Archipelago are popular destinations for tourism, offering opportunities for eco-tourism, water sports, and cultural experiences. The tourism industry in these regions contributes to the country's economic growth and development, providing employment and generating revenue for local communities.
In conclusion, the regions of Venezuela contribute significantly to the country's economy, each playing a unique role in shaping its economic landscape. From agriculture and mining to tourism and oil production, the regions of Venezuela offer a diverse array of economic activities and opportunities.
What makes Venezuela's biodiversity unique?
Venezuela is known for its rich and diverse biodiversity, with a wide array of ecosystems and species found throughout the country's regions. From the lush rainforests of the Amazon to the vast plains of the Llanos, Venezuela's biodiversity is a testament to the country's unique geography and climate.
The Amazon Region is home to one of the most biologically diverse ecosystems on the planet, with a vast array of plant and animal species. The region's rainforests provide essential habitats for species such as jaguars, pink river dolphins, and macaws, as well as countless species of insects and amphibians.
The Orinoco Delta, with its intricate network of waterways and wetlands, supports a rich array of wildlife and plant species. The region's diverse ecosystems play a crucial role in supporting Venezuela's biodiversity and maintaining the health of the surrounding environment.
The Andes and Guayana Regions offer unique ecosystems and landscapes, with diverse flora and fauna. The Andes' mountainous terrain and the Guayana's plateaus and waterfalls provide essential habitats for species such as condors, spectacled bears, and giant anteaters.
The Caribbean Coast and Los Roques Archipelago are home to vibrant marine ecosystems, with coral reefs, sea turtles, and a variety of fish species. The region's clear waters and abundant marine life make it a prime location for underwater exploration and eco-tourism.
In conclusion, Venezuela's biodiversity is a testament to the country's unique geography and climate, with a wide array of ecosystems and species found throughout the regions. From the lush rainforests of the Amazon to the vibrant marine life of the Caribbean Coast, Venezuela's biodiversity is a valuable and essential part of the country's natural heritage.
What challenges do the regions of Venezuela face?
The regions of Venezuela face a variety of challenges that impact their economic, environmental, and social development. These challenges include political instability, economic uncertainty, environmental degradation, and social inequality.
Political instability and economic uncertainty have significantly impacted Venezuela's regions, affecting their ability to attract investment and develop sustainable economic activities. The country's reliance on oil exports has led to economic volatility, with fluctuations in global oil prices affecting the regions' economic stability and growth.
Environmental degradation is a significant challenge for Venezuela's regions, with deforestation, pollution, and habitat destruction threatening the country's rich biodiversity and natural resources. The Amazon Region, in particular, faces significant threats from illegal logging, mining, and agricultural expansion, which impact the region's ecosystems and indigenous communities.
Social inequality is another challenge faced by Venezuela's regions, with disparities in access to education, healthcare, and essential services affecting the well-being and development of local communities. Indigenous communities, in particular, face significant challenges in preserving their cultural heritage and accessing resources and opportunities.
In conclusion, the regions of Venezuela face a variety of challenges that impact their economic, environmental, and social development. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts and sustainable solutions that prioritize the well-being and development of local communities and the preservation of the country's natural and cultural heritage.
Tourism in Venezuela: Discovering its Regions
Tourism in Venezuela offers a diverse array of experiences and opportunities, with each region providing its own unique blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and recreational activities. From the stunning beaches of the Caribbean Coast to the lush rainforests of the Amazon, Venezuela's regions offer something for every type of traveler.
The Caribbean Coast and Los Roques Archipelago are popular destinations for beach lovers and water sports enthusiasts, offering opportunities for snorkeling, scuba diving, sailing, and relaxation. The region's vibrant coastal towns and cities provide a blend of cultural experiences, traditional cuisine, and lively festivals.
The Andes Region offers a mix of outdoor adventure and cultural exploration, with opportunities for hiking, mountain climbing, and exploring picturesque towns and cities. The region's rich cultural heritage and traditional festivals provide a glimpse into the vibrant traditions and customs of the Andean people.
The Amazon and Orinoco Delta Regions offer eco-tourism and adventure travel opportunities, with pristine landscapes, diverse ecosystems, and indigenous cultures to explore. Visitors can trek through rainforests, navigate waterways, and learn about traditional ways of life and sustainable living.
The Guayana and Llanos Regions offer opportunities for wildlife viewing, cultural experiences, and adventure travel. Visitors can explore national parks, discover unique ecosystems, and learn about the region's rich cultural heritage and economic significance.
In conclusion, tourism in Venezuela offers a diverse array of experiences and opportunities, with each region providing its own unique blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and recreational activities. From stunning beaches and lush rainforests to vibrant cities and traditional cultures, Venezuela's regions offer something for every type of traveler.
FAQs about the Regions of Venezuela
1. What are the main regions of Venezuela?
Venezuela is divided into several main regions, including the Andes Region, Llanos Region, Amazon Region, Caribbean Coast, Orinoco Delta, Central Region, Guayana Region, Maracaibo Basin, and Los Roques Archipelago. Each region offers its own unique blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and economic significance.
2. How does the geography of Venezuela's regions impact its biodiversity?
The diverse geography of Venezuela's regions, including mountains, plains, rainforests, and coastlines, contributes to the country's rich biodiversity. Each region provides unique ecosystems and habitats that support a wide array of plant and animal species, making Venezuela one of the most biologically diverse countries in the world.
3. What role do indigenous communities play in the regions of Venezuela?
Indigenous communities play a vital role in the regions of Venezuela, particularly in the Amazon and Orinoco Delta Regions. These communities have lived in harmony with the land for centuries, preserving their traditional ways of life and cultural practices. They offer valuable insights into sustainable living and biodiversity conservation.
4. What are some popular tourist activities in Venezuela's regions?
Popular tourist activities in Venezuela's regions include beach relaxation and water sports on the Caribbean Coast, hiking and cultural exploration in the Andes, eco-tourism and adventure travel in the Amazon and Orinoco Delta, and wildlife viewing and cultural experiences in the Llanos and Guayana Regions.
5. How do the regions of Venezuela contribute to the country's economy?
The regions of Venezuela contribute significantly to the country's economy through agriculture, mining, oil production, and tourism. The Llanos Region is known for its agricultural productivity, the Guayana Region for its mineral resources, the Maracaibo Basin for its oil industry, and the Caribbean Coast and Los Roques Archipelago for tourism.
6. What challenges do the regions of Venezuela face?
The regions of Venezuela face challenges such as political instability, economic uncertainty, environmental degradation, and social inequality. These challenges impact the regions' development and well-being, requiring collaborative efforts and sustainable solutions to address them.
Conclusion: Embracing Venezuela's Regional Diversity
The regions of Venezuela offer a captivating blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and economic significance. From the towering mountains of the Andes to the lush rainforests of the Amazon, and from the vibrant Caribbean Coast to the vast plains of the Llanos, each region presents its own unique story and treasures to discover. Understanding the regions of Venezuela is essential for appreciating the country's diverse landscapes, cultural heritage, and economic opportunities.
Whether you're a nature enthusiast seeking adventure, a cultural traveler interested in exploring traditional customs, or someone looking to learn more about Venezuela's economic landscape, the regions of Venezuela have something to offer everyone. By embracing the diversity and richness of these regions, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of this remarkable country.
As we continue to explore and learn about the regions of Venezuela, it is essential to prioritize sustainable development, cultural preservation, and environmental conservation. By working together to address the challenges faced by these regions, we can ensure a brighter and more prosperous future for Venezuela and its people.